Introduction Of Matic blockchain
The Matic Network, now known as Polygon, is a Layer 2 scaling solution built on the Ethereum blockchain. It aims to solve the scalability and usability challenges faced by the Ethereum ecosystem by offering faster and cheaper transactions.
Matic achieves this by using a sidechain-based approach that leverages the Plasma framework. This allows Matic to process thousands of transactions per second, making it a much faster and more cost-effective solution for dApps built on Ethereum. By processing transactions off-chain, Matic can also reduce the load on the Ethereum network and lower gas fees.
History of Matic Blockchain
A group of blockchain engineers, including Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, and Anurag Arjun, established The Matic Network, currently referred to as Polygon, in 2017. Initially known as Matic Network, the project's objective was to increase the Ethereum blockchain's scalability and resolve the security, scalability, and decentralisation trilemma.
By holding an initial exchange offering (IEO) in April 2019, Matic Network was able to raise $5 million from investors including Binance, Coinbase Ventures, and Digital Currency Group. A PoS consensus method and the Plasma framework were used by the project to handle transactions off-chain before launching its mainnet in June 2020.
The Matic Network changed its name to Polygon in 2021 to represent its progress beyond a straightforward scaling solution for Ethereum. Polygon wants to develop into a complete multi-chain solution that supports communication between several blockchain networks.
With more and more dApps and blockchain applications utilising Polygon's platform, the company has experienced considerable growth in the blockchain sector. Decentralised finance (DeFi) and non-fungible token (NFT) ecosystems will thrive with the help of a $100 million fund, Polygon announced in May 2021.
The Matic Blockchain technology
To achieve its scalability, security, and interoperability, the Matic blockchain—now known as Polygon—is built on a number of different technologies. The Matic blockchain uses a number of the following essential technologies:
Plasma framework: To handle transactions off-chain, the Matic network makes use of the Plasma framework, a Layer 2 scalability solution for Ethereum. This enables it to process thousands of transactions per second, greatly enhancing transaction speed and lowering rates.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism: The PoS consensus mechanism used by Matic selects validators based on the number of Matic tokens they own and are prepared to stake. This guarantees network security while being more environmentally friendly and energy-efficient than Ethereum's energy-intensive Proof-of-Work (PoW) process.
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatibility: The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which enables programmers to use the same programming languages and tools when building on Ethereum, is completely compatible with the Matic network.
Interoperability: The interoperability of Polygon with other blockchains enables dApps created on the platform to communicate with other networks. The Polygon Bridge from Polygon makes it possible for users to transfer assets between Ethereum and other supported networks.
Polygon SDK: A software development kit called the Polygon SDK gives programmers the resources and tools they need to create dApps for the Polygon network. It has features including a PoS consensus method, Plasma framework implementation, and Web3.js integration.
Zero-knowledge proofs: Zero-knowledge proofs are supported by Polygon, enabling secure and private transactions without disclosing any information about the parties or the transaction itself.
The workings of the matic blockchain
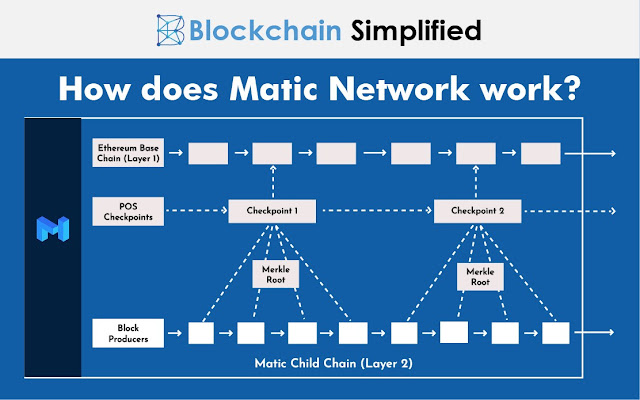
The Polygon blockchain, formerly known as Matic, serves as the Ethereum network's Layer 2 scalability solution. It processes transactions off-chain using a sidechain-based method, which lightens the strain on the Ethereum network and enhances scalability.
Depositing funds: Users must first deposit funds from the Ethereum network onto the Matic network in order to use it. Sending cryptocurrency or ERC-20 tokens to a particular deposit address on the Ethereum network accomplishes this.
Plasma framework: After the money is deposited, the Matic network processes transactions off-chain using the Plasma framework. Due to this, it can process thousands of transactions per second, greatly enhancing transaction speed and lowering costs.
PoS consensus mechanism: Using a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, validators are selected for a Matic network based on the number of Matic tokens they own and are prepared to stake. The Matic network needs validators to validate transactions and add new blocks.
Security: The Matic network frequently checks its state on the Ethereum mainnet to guarantee network security. This implies that the Matic network can be restored to the most recent checkpoint in the event of a malfunction.
Withdrawing funds: Users only need to transmit money back to the Ethereum network in order to withdraw money from the Matic network. Users can transfer money between the two networks with ease thanks to the Matic network's speedy and safe money transfers.
Why the Matic Blockchain is a Game-Changer for Ethereum?
Due to its capacity to increase the scalability and usability of the network, the Matic blockchain, now referred as as Polygon, is a game-changer for the Ethereum ecosystem. Here are a few explanations:
Faster and cheaper transactions: The sidechain-based methodology used by the Matic network enables it to perform thousands of transactions per second. Compared to Ethereum, which can be slowed down by congestion and expensive petrol expenses, this makes it significantly faster and more affordable. Matic decreases gas costs and lightens the stress on the Ethereum network by processing transactions off-chain.
Improved user experience: The quicker and less expensive transactions on Matic result in a significantly improved user experience for d-Apps created on the platform. Users can benefit from very instantaneous transaction speeds and lower fees, which makes using and interacting with decentralized applications more appealing.
Eco-friendly consensus mechanism: Unlike the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus process used by Ethereum, Matic uses a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. As a result, Matic can offer a more ecologically friendly and long-lasting solution for blockchain transactions.
Interoperability: Matic is made to work with other blockchains, allowing for more liquidity across many networks. This enables d-Apps created on Matic to communicate with other blockchains, simplifying the development of cross-chain apps and expanding the market for De-Fi and NFT platforms.
Commitment to innovation: Matic has a proven record of innovation, constantly advancing its technology and boosting its functionalities. Matic's recent purchase of Hermez Network is evidence of its dedication to improving Layer 2 scaling solutions and growing its ecosystem.
The application of Matic blockchain
You need a wallet that supports the Matic network in order to use the Polygon blockchain, formerly known as Matic. The general procedures for utilizing the Matic blockchain are as follows:
Get a wallet: A wallet that works with the Matic network is required. Meta Mask, My-Ether-Wallet, and Trust Wallet are a few examples. Make sure the wallet you select can connect to your web browser or mobile device and supports the Matic network.
Transfer funds to your Matic wallet: You must move money to a wallet that is compatible with the Matic network once you have one. Sending Ethereum or ERC-20 tokens from your Ethereum wallet to your Matic wallet will do this.
Use d-Apps on the Matic network: When you have money in your Matic wallet, you can use decentralized applications (d-Apps) created on the Matic network. Aavegotchi, Quick-Swap, and Poly-cat are a few of the well-known d-Apps on the Matic network.
Transfer funds back to Ethereum: To transfer money from your Matic wallet back to the Ethereum network, send it to your Ethereum wallet once more. Use the Polygon Bridge, which enables asset movement between the two networks, to do this.
Explore the network: A flexible platform with numerous use cases is the Matic blockchain, currently known as Polygon. The network can be used to create your own d-Apps or to search for d-Apps that catch your attention.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Matic Network is a Layer 2 scaling solution that offers d-Apps built on Ethereum a quick, safe, and affordable option. For programmers wishing to create scalable and creative blockchain applications, its architecture, PoS consensus process, interoperability features, and support for the Ethereum Virtual Machine make it a flexible platform.








Comments
Post a Comment